Disk usage in Linux refers to the amount of space utilized and available on a disk or file system. Monitoring disk usage is crucial for managing storage resources effectively, understanding how much space is being consumed by files, directories, and the overall system.
Linux provides various commands and utilities to assess disk usage:
Table of Contents
df command:
The df command in Linux stands for “Disk Free.” It is used to display information about the disk space usage on file systems. This command shows details such as the total amount of disk space, the amount of space used, available space, filesystem types, and their respective mount points.
When you run df without any arguments, it lists information about all mounted filesystems
Displays information about disk space usage of file systems. It shows the amount of disk space used and available on mounted file systems.
df -h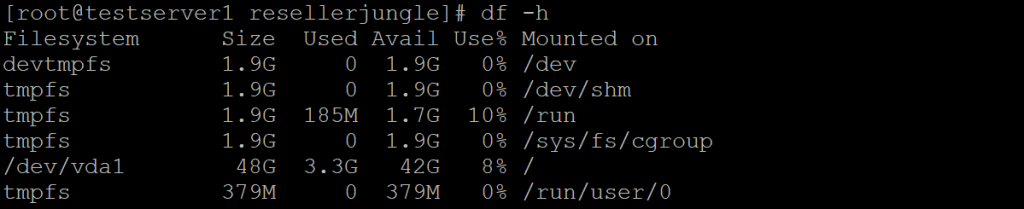
du (disk usage) command:
The du command in Linux stands for “Disk Usage.” It is used to estimate and display the disk space used by files and directories. This command helps users and system administrators identify the disk space consumption of specific directories or files.
By default, when you use du without any additional options, it provides the disk usage of the current directory and its subdirectories
Estimates file and directory space usage. It shows the sizes of directories and files.
du -h /path/to/directorydu -h /home/resellerjungle
ncdu command:
The ncdu command in Linux stands for “NCurses Disk Usage.” It’s a disk usage analyzer tool that provides a more interactive and intuitive way to visualize and manage disk space usage within the terminal.
Unlike traditional commands like du that display disk usage information in a static text format, ncdu presents a visual representation of disk usage using an interactive, text-based user interface (NCurses).
NCurses Disk Usage is a command-line utility to interactively view and manage disk usage. It provides a top-like interface to navigate through directories and their sizes.
du /path/to/directorydu /home/resellerjungle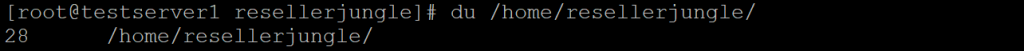
du -sh command:
The du -sh command in Linux is used to summarize the total disk usage of a specific directory or file in a human-readable format.
Summarizes the total disk usage of a particular directory in a human-readable format.
du -sh /path/to/directoryfind command:
The find command in Linux is a powerful utility used for searching and locating files and directories within a specified directory hierarchy. It allows users to search for files based on various criteria such as filename, size, modification date, ownership, and permissions.
Helps find files and directories based on various criteria such as size.
find /path/to/directory -type f -size +100Mls command:
The ls command in Linux is used to list the contents of a directory. It shows the files and directories within the specified directory, providing details such as file permissions, ownership, size, and modification time.
Although primarily used for listing files, the -l option with ls can show file sizes, ownership, permissions, and timestamps.
ls -l /path/to/filediskutil command:
The diskutil command is a command-line utility available on macOS systems. It is used for managing disks, volumes, partitions, and related storage devices. diskutil provides various functionalities for disk management, including formatting, partitioning, repairing disks, mounting/unmounting volumes, and more.
On macOS systems, diskutil is a command-line utility for querying and manipulating local disks and volumes.
diskutil liststat command:
The stat command in Linux and Unix systems is used to display detailed information about files, including file status, metadata, and file system information. It provides various details about a file such as access permissions, inode number, file type, size, timestamps (last access, modification, and change times), and more.
Retrieves detailed file or file system status.
stat /path/to/filefdisk command:
The fdisk command in Linux and Unix-based systems is a command-line utility used for disk partitioning. It allows users to create, delete, modify, and display information about partitions on a hard disk. fdisk is a powerful tool but requires careful usage as it deals with disk partitions and can potentially lead to data loss if not used correctly.
A command-line utility for disk partitioning. It’s used to view, create, delete, change, or resize partitions on a hard drive.
do fdisk -lparted command:
The parted command in Linux is a powerful command-line utility used for disk partitioning and managing disk partitions. It is a versatile tool that allows users to create, delete, resize, move, and manipulate disk partitions on hard drives. parted is especially useful for working with modern disk formats like GUID Partition Table (GPT) and is more flexible compared to older utilities like fdisk.
Another command for partition manipulation, providing functionalities similar to fdisk but with a different interface.
sudo parted /dev/sdX printRemember to use these commands carefully, especially when dealing with system-level operations like disk partitioning, to avoid data loss or accidental modifications. Use man followed by the command name for more detailed information and available options.




