Files are one of the most important objects of any operating system and Linux is not an exception. Files provide a reliable way of storing data in a persistent manner.
Linux uses plain text files to store important configurations. For example, the /etc/hosts file stores static table lookup for hostnames, the /etc/crontab file contains instructions for the cron daemon, and so on.
Certainly, we can use graphical tools to create files. However, the same can be achieved using the command line interface as well.
Echo: The echo command in Linux is used to display text or output to the terminal or to redirect it to a file. It’s a fundamental command that’s often used in scripts or when interacting with the command line.
Touch: The touch command is used to create new empty files or update the timestamps (access and modification times) of existing files. It’s a versatile command that serves multiple purposes related to file handling.
Tee: In Linux, the tee command is used to read the standard input and write it to both the standard output (usually the terminal) and one or more files simultaneously. This command is particularly useful when you want to view the output of a command on the screen while also saving it to a file for later use.
Cat: The cat command is a versatile utility used to concatenate and display the content of files. Despite its name, which stands for “concatenate,” cat is primarily used for displaying text files, creating new ones, combining copies of them, and redirecting output in the terminal.
In this easy-to-follow guide, we will discuss various ways of creating a file in Linux.
Table of Contents
1. Create an Empty File Using > Redirection Operator
In Linux, the redirection operator (>) is used to redirect the output of a command to a file instead of displaying it on the terminal.
The same (>) operator is also used to create a file if it doesn’t exist already. However, it makes the file empty if it exists already. Hence one should be very careful while using the redirect operator.
> resellerjungle.txt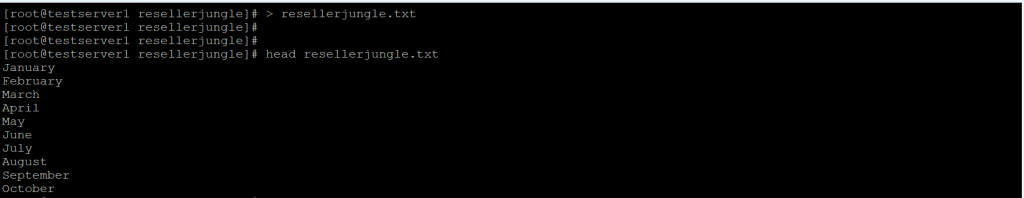
2. Create File and Write Content Using > Redirection Operator
Sometimes, we want to create a non-empty file quickly. In such cases, you can use the output redirection operator (>) to create a file and write content to it using the echo command as shown.
echo "resellerjungle.com is a Best Business Web Hosting" > resellerjungle.txt
head resellerjungle.txt
It is important to note that in this example, we have used the echo command to create a file. However, we can redirect the output of the other Linux commands as well to create a file.
Also, it is important to note that the > redirection operator is used to overwrite the contents of an already existing file, which cause data loss if the operation is performed carelessly.
In such a case, we can use the >> redirection operator, which is used to append the contents to the existing file.
echo "resellerjungle.com is a #1 Business Web Hosting" >> resellerjungle.txt
head resellerjungle.txt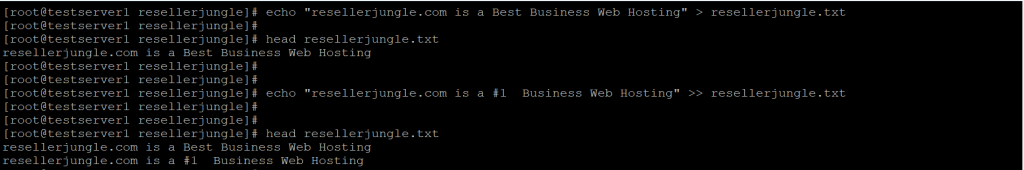
In the above output, we can see that the new line gets appended at the end of the file.
It is worth noting that, just like the redirection operator, the append operator will also create an empty file if it doesn’t exist already.
3. Create Files Using touch Command
One more way of creating a file is using the touch command, which offers the safest way of creating an empty file because it never overwrites the existing file. Instead, it just updates the time stamp (access time and modification time) of the existing file.
touch resellerjungle.txt
4. Create Files Using tee Command
Similar to the redirection operator we can also use the tee command to create a file. The tee command writes the output of the command to the standard output stream as well as the file.
For example, to create a file named “resellerjungle.txt“, use the tee command, which will be ready to accept input.
tee resellerjungle.txt
If you want to overwrite the content of a file using the tee command, you can use the following command
echo "Overwrite file using the tee command" | tee resellerjungle.txt
head resellerjungle.txt
In this example, we can observe that the tee command overwrites the contents of the resellerjungle.txt file which was created and updated in earlier examples.
To append the contents to the existing file, use the -a option of the tee command, which allows us to append the data at the end of the existing file.
echo "Append data using the tee command" | tee -a resellerjungle.txt
head resellerjungle.txt
5. Create a File Using cat Command
We can use the combination of the cat command and redirection operator to create a file. For example, the below command creates a new file if it doesn’t exist already.
cat > resellerjungle.txt
Here, the terminal waits infinitely for the user input. We have to press Ctrl + D after entering the required text to save the contents to the file:
The main advantage of this approach is that it allows us to create a multi-line file using an interactive way. Just like the redirection operator, we have to use this method very carefully as it overwrites the existing file.
In a similar way, we can use the combination of the cat command and append operator to append the contents at the end of the existing file.
cat >> resellerjungle.txt
Just like in the previous example, we have to press Ctrl + D to append the contents to the file after entering the required text.
In this guide, we discussed how to create a file using the Linux command line interface. Linux beginners can use one of the methods to create a file from the terminal.
We hope you’ve found this useful!




