A Yum plugin is a modular piece of software that extends the functionality of the Yum package manager in RPM-based Linux distributions, such as CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux. These plugins provide additional features, optimizations, or customizations to enhance the package management experience.
Yum plugins can perform various tasks, including:
- Speeding up package downloads: Plugins like
fastestmirrorcan determine the fastest mirror from which to download packages, optimizing download times. - Enhancing security: Plugins like
yum-plugin-securitycan provide information about security vulnerabilities associated with installed packages. - Enabling additional repositories: Some plugins help manage and enable third-party repositories, expanding the available software packages.
- Automating tasks: Plugins can automate specific tasks, such as cleaning up obsolete packages or handling dependencies more efficiently.
- Adding new commands or options: Plugins can introduce new commands or options to the Yum command-line interface, allowing users to perform tasks beyond the basic package installation and removal.
Examples of Yum plugins include fastestmirror, versionlock, security, post-transaction-actions, and more.
You can list the available Yum plugins on your system using the following command:
yum list | grep ^yum-plugin
To enable, disable, or configure a specific plugin, you can use the yum-config-manager command or edit the configuration files in the /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/ directory.
Keep in mind that the availability of plugins may vary between different Linux distributions and Yum versions.
To see all active plug-ins, run a yum command on the terminal. From the output below, you can see that the fastestmirror plug-in is loaded.
yum search nginx
Table of Contents
Enabling YUM Plugins
Enabling Yum plugins refers to the process of activating additional modular components that extend and enhance the functionality of the Yum package manager on RPM-based Linux systems.
These plugins provide supplementary features, optimizations, and customization options to improve the overall package management experience.
Enabling Yum plugins allows users to access and leverage these additional capabilities for tasks such as speeding up package downloads, enhancing security, or automating specific functions within the package management system.
To enable yum plug-ins, ensure that the directive plugins=1 (1 meaning on) exists under the [main] section in the /etc/yum.conf file
vi /etc/yum.conf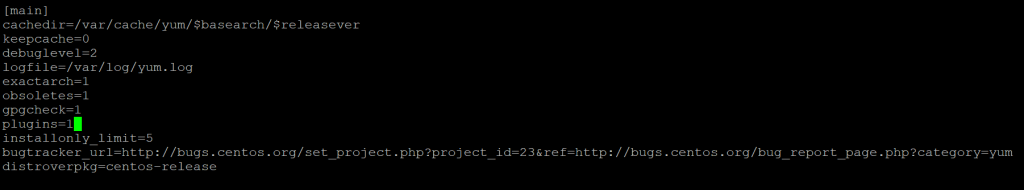
Disabling YUM Plugins
Disabling Yum plugins involves deactivating specific modular components that extend the functionality of the Yum package manager on RPM-based Linux systems.
When a Yum plugin is disabled, it ceases to influence or modify the behavior of the package manager. This action can be useful in scenarios where users want to revert to the default configuration, eliminate certain features, or troubleshoot issues related to a particular plugin.
By disabling Yum plugins, users have control over which additional functionalities are active or inactive during the package management processes on their Linux systems.
To disable yum plug-ins, simply change the value above to 0 (meaning off), which disables all plug-ins globally.
plugins=0At this stage, it is useful to note that:
- Since a few plug-ins (such as product-id and subscription-manager) offer fundamental yum functionalities, it is not recommended to turn off all plug-ins especially globally.
- Secondly, disabling plug-ins globally is allowed as an easy way out, and this implies that you can use this provision when investigating a likely problem with yum.
- Configurations for various plug-ins are located in /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/.
- Disabling plug-ins globally in /etc/yum.conf overrides settings in individual configuration files.
- And you can also disable a single or all yum plug-ins when running yum, as described later on.
Installing and Configuring Extra YUM Plugins
You can view a list of all yum plug-ins and their descriptions using this command.
yum search yum-plugin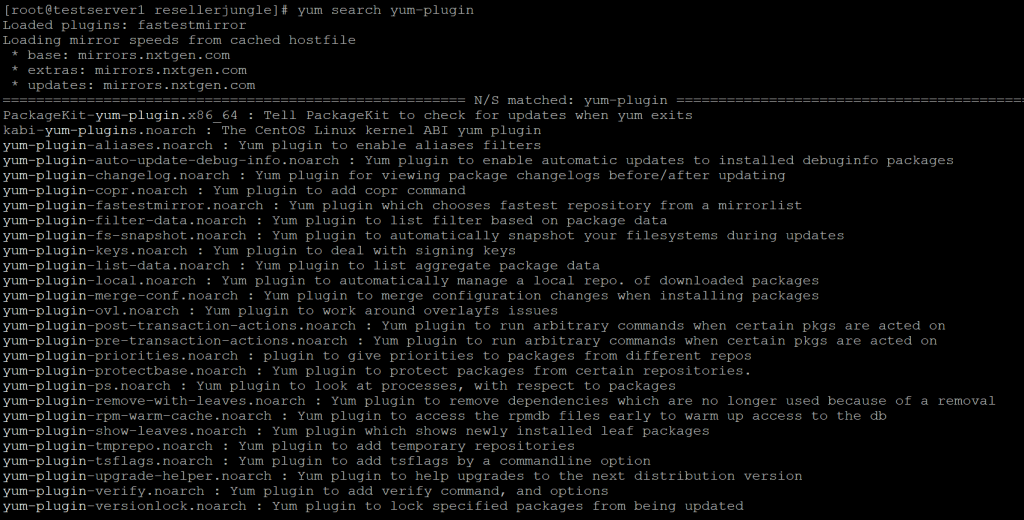
To install a plug-in, use the same method for installing a package. For instance we will install the changelog plug-in which is used to display package changelogs before/after updating.
yum install yum-plugin-changelog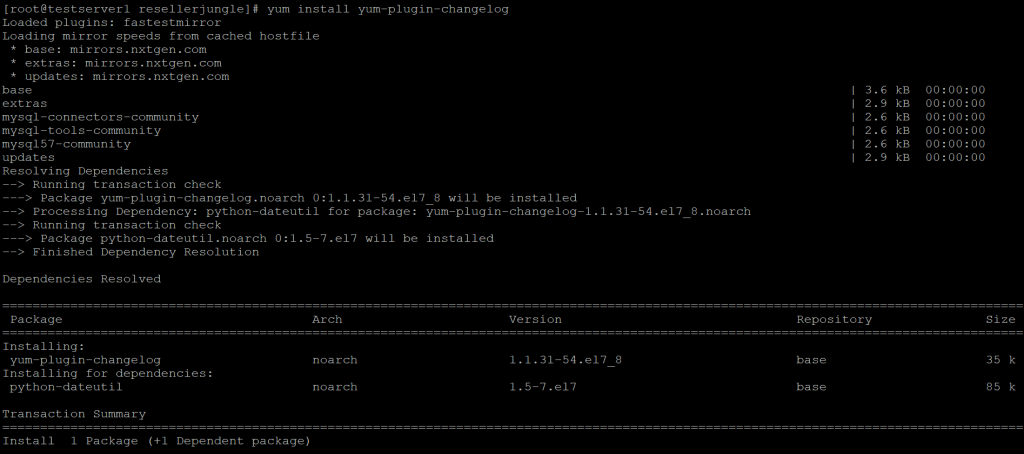
Once you have installed, changelog will be enabled by default, to confirm take look into its configuration file.
vi /etc/yum/pluginconf.d/changelog.confNow you can view the changelog for a package (httpd in this case) like below.
yum changelog httpdDisable YUM Plugins in Command Line
As stated before, we can also turn off one or more plug-ins while running a yum command by using these two important options.
.–noplugins – turns off all plug-ins
.–disableplugin=plugin_name – disables a single plug-ins
You can disable all plug-ins as in this yum command.
yum search --noplugins yum-plugin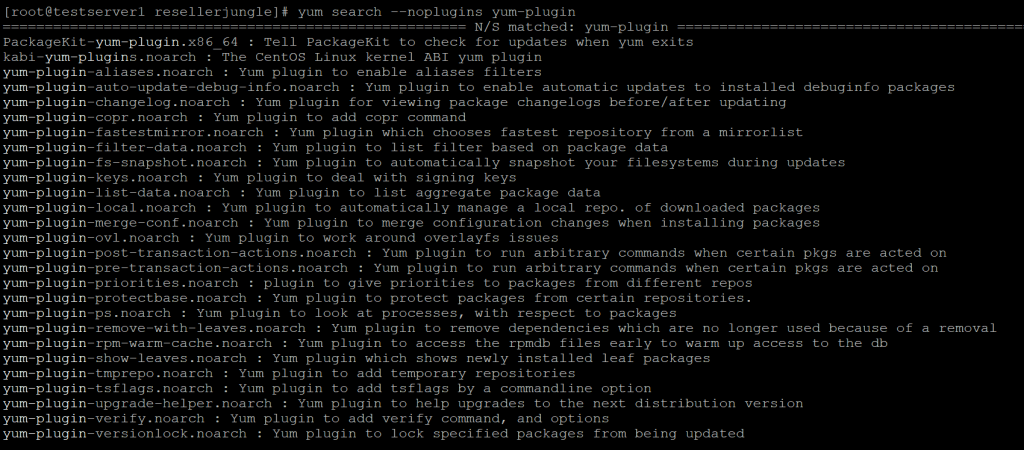
The next command disables the plug-in, fastestmirror while installing httpd package.
yum install --disableplugin=fastestmirror httpd
Now, you’ve an idea on enable/ disable and install yum plugins in CentOs / RHEL




