The cat command in Linux is a command-line utility that is used to concatenate and display the content of files. The name “cat” stands for concatenate, but it is commonly used for other purposes as well.
The primary function of the cat command is to display the contents of one or more files to the terminal. It can also be used to concatenate the content of multiple files and create a new file.
It’s worth noting that while cat is a simple and versatile command, there are other commands like less, more, and head/tail that offer additional features such as pagination, scrolling, and viewing specific parts of a file.
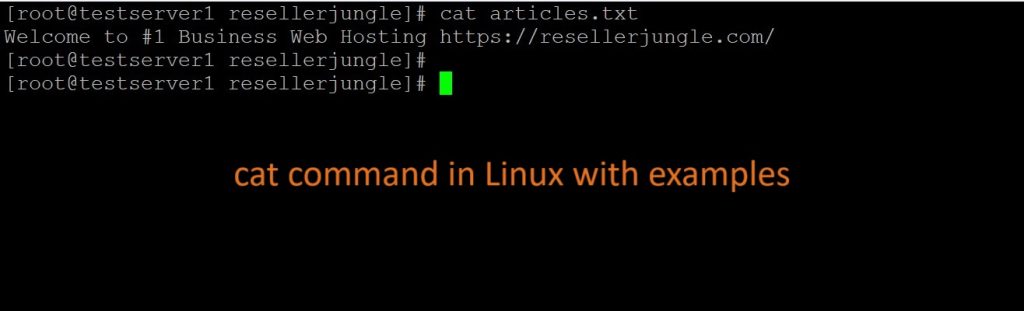
Table of Contents
Basic Syntax of cat Command
The basic syntax of the ‘cat’ command is as follows:
cat [OPTION] [FILE]Here,
[OPTION] : represents various command-line options.
[FILE] : the name of the file(s) to be processed. Let’s explore some of the common uses of ‘cat’ along with examples.
Practical Examples of Cat Command in Linux
1.How to View the Content of a Single File in Linux
The most basic use of ‘cat’ is to display the contents of a file on the terminal. This can be achieved by simply providing the filename as an argument:
cat file_nameExample: If our file_name = articles.txt
cat articles.txt
Note: ls command is used to display all files and directories in the current location.
2.How to View the Content of Multiple Files in Linux
Syntax:
cat file_name1 file_name2Example: If we have two files , file1 and file2.
cat file1 file2
3.How to View Contents of a File preceding with Line Numbers in Linux
Adding the -n option to cat introduces line numbers, making it convenient to identify and reference specific lines within the file.
Syntax:
cat -n file_nameExample: If our file_name is file2.
cat -n file2
Here, the cat command, used with the redirection (>), allows you to create a new file named “articles” and input content directly into it. The subsequent ls command lists all files in the current location.
4.How to Create a file and add content in Linux Using cat Command
If you want to create a new file or overwrite an existing file with new content, you can use ‘cat’ with the output redirection (>):
Syntax:
cat > newfile_nameExample: If we want to create a newfile_name = articles.
cat >articleslsThis will allow you to type text directly into the terminal, and when you press Ctrl + D, the entered text will be saved to new_file.txt.
ls command is used to display all files and directories in the current location.
5.How to Copy the Contents of One File to Another File in Linux
As the name suggests, ‘cat’ can concatenate multiple files into a single file. This example illustrates how to copy the entire content of “file1” into “file2” using the cat command along with redirection (>).
Syntax:
cat file1.txt file2.txt > merged_file.txt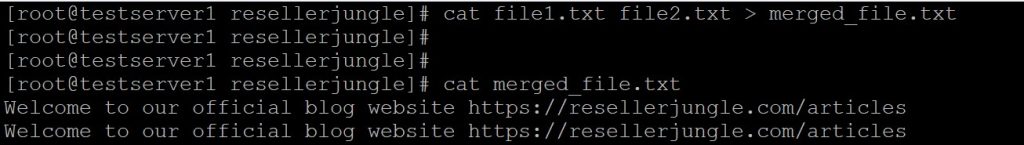
This command combines the content of file1.txt and file2.txt into a new file named merged_file.txt.
6.Cat command can suppress repeated empty lines in output
The -s option comes in handy when dealing with files containing repeated empty lines. It suppresses these repetitions, providing a cleaner output.
Syntax:
cat -s file_nameOutput

Will suppress repeated empty lines in output
7.How to Append the Contents of One File to the End of Another File
If you want to add the content of one file to another, ‘cat’ can be used along with the append (>>) operator:
Syntax:
cat file_name1 >> file_name2Example:
cat file1 >> file2This will append the content of file1 to the end of file2
8.How to Display Content in Reverse Order Using tac Command in Linux
The ‘tac’ command is the reverse of ‘cat’ and is used to display the content of a file in reverse order. The syntax is simple:
Syntax:
tac file_nameExample:
This command will print the content of ‘file2’ in reverse order, displaying the last line first, followed by the second-to-last line, and so on.
tac file29.How to Highlight the End of Line in Linux
The ‘-E’ option in the ‘cat’ command is used to highlight the end of each line.
Syntax:
cat -E "filename"Output:
This will display the content of ‘articles1’ with a ‘$’ character at the end of each line, indicating the line’s terminate.
10.-A Command Line Option in cat Command in Linux
The ‘-A’ option allows you to combine the effects of ‘-v’, ‘-E’, and ‘-T’ options. Instead of writing ‘-vET’ in the command, you can use ‘-A’:
Syntax:
cat -A "filename"This will display the content of ‘filename’ with non-printing characters visible, line endings highlighted, and tabs displayed as ‘^I’.




